04. FMCW
Header Text
FMCW
L1A25 FMCW
Features of FMCW
FMCW radar (Frequency-Modulated Continuous Wave radar) is a special type of radar sensor which radiates continuous transmission power. FMCW radar’s ability to measure very small ranges to the target as well as its ability to measure simultaneously the target range and its relative velocity makes it the first choice type of radar for automotive applications.
FMCW Chirps
ND313 Andrei Intv 14 What Is A Chirp
FMCW waveform
FMCW waveform
source : emagtech
Chirp Sequence
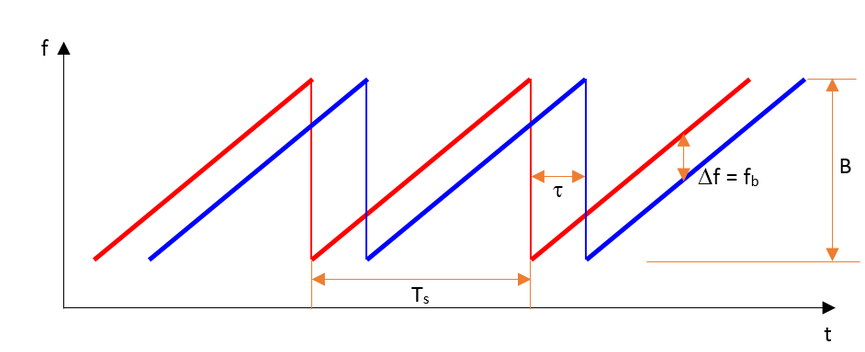
A Frequency Modulated Continous Wave (FMCW) is a signal in which the frequency increases/decreases with time. They are also referred to as upramps and downramps. The two most common waveform pattern used for FMCW radars are sawtooth and triangular. The sawtooth waveform generally uses just the upramps, whereas the triangular waveform uses both upramps and downramps.
Each chirp is defined by its slope. The slope is given by its chirp frequency bandwidth B or B_{sweep} (y-axis) and its chirp time T_s (x-axis). Hence,
The range resolution requirement decides the B , whereas the maximum velocity capability of a radar is determined by the chirp time T_s . We will discuss this in more detail in later sections.
One chirp sequence or segment comprises of multiple chirps. Each chirp is sampled multiple times to give multiple range measurements and radar transmits in order to measure doppler velocity accurately.
In the course project you will sample each chirp 1024 times and send 128 of these chirps to estimate the range and doppler velocity. So, the segment in this case would comprise of 128 chirps.